The McKinsey 2022 Global Payments Report presents a detailed analysis of the 2021 results and the insights they reveal, including regional and country-level nuances. The report’s later chapters offer perspectives on areas where payments leaders’ actions will help determine market share shifts and the role of payments in the broader financial ecosystem.
Excerpts below, download the entire report here

First, the report examines a rapidly growing payments service: embedded finance, which involves the integration of a financial product into a broader customer journey. Brick-and-mortar versions have existed for decades in the form of auto loans at dealerships, sales financing at appliance retailers, and private-label credit cards at retail chains. Software companies are now partnering with banks and technology (or banking-as-a-service) providers to create similar seamless and convenient digital experiences. Leaders are already emerging in the race to provide banking infrastructure for embedded finance, and this chapter describes how incumbents and new entrants still have time to claim a share of this market.

In the next chapter, the report takes a fresh look at the early-stage development of central-bank digital currencies (CBDCs), which is occurring around the globe. Along with summarizing the various models under consideration, this chapter outlines the risks, opportunities, and potential paths forward for stakeholders and explains why we believe that the most promising scenarios involve public-private partnerships in which commercial banks play a material role.
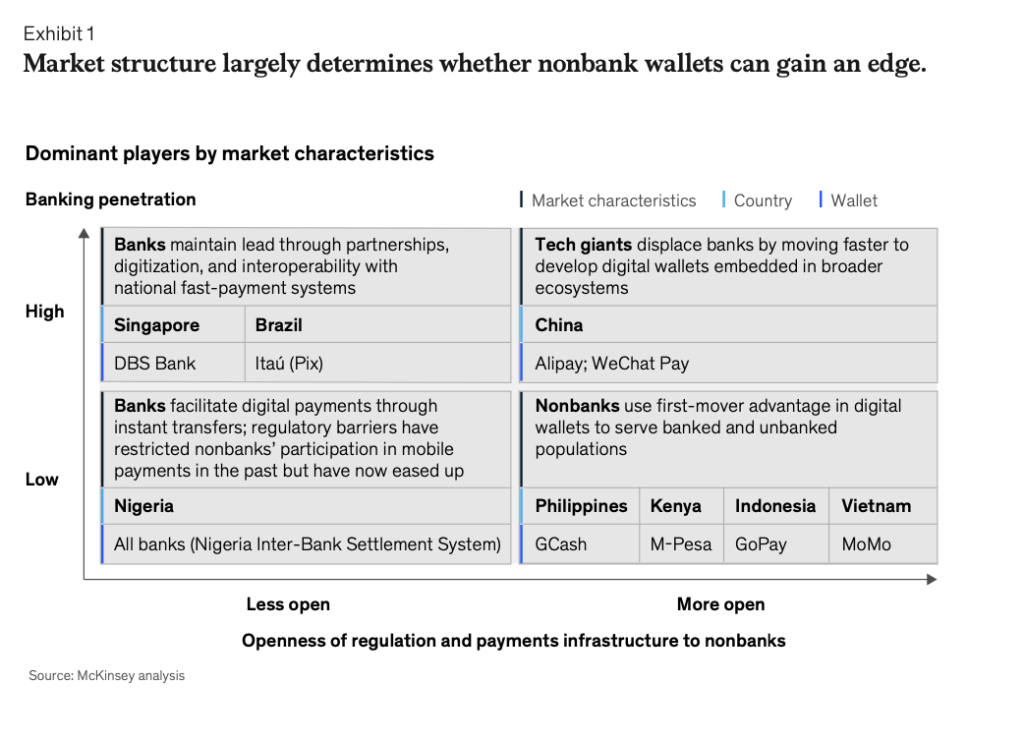
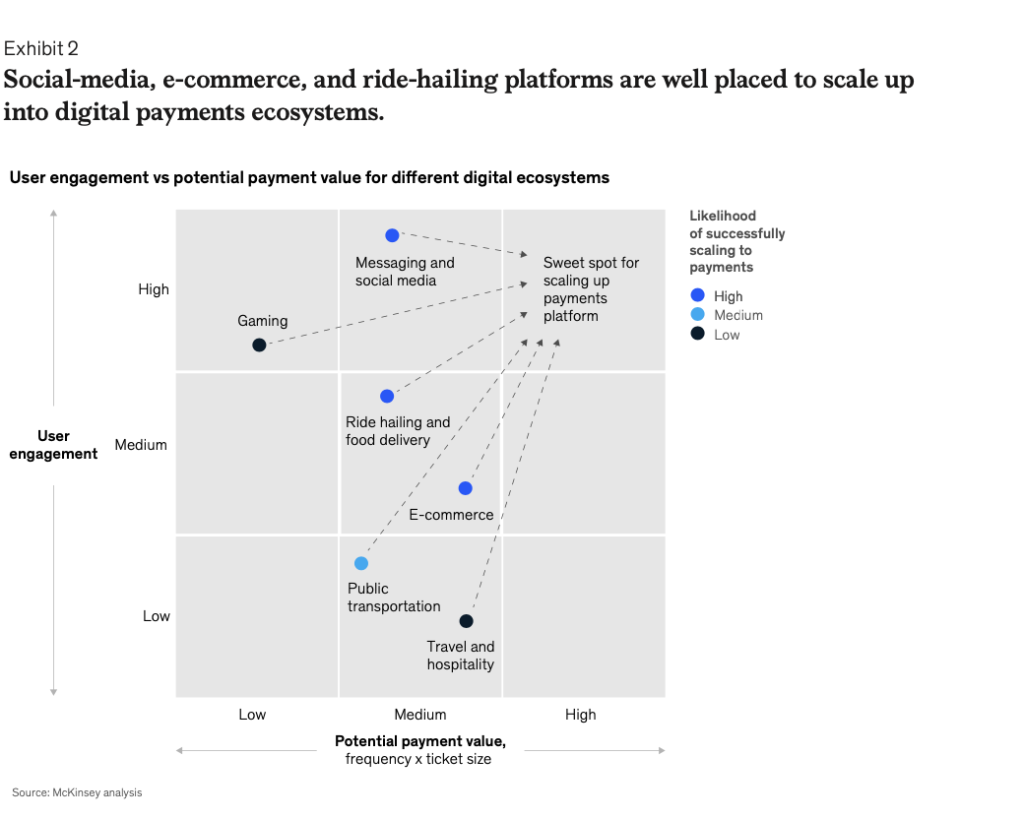
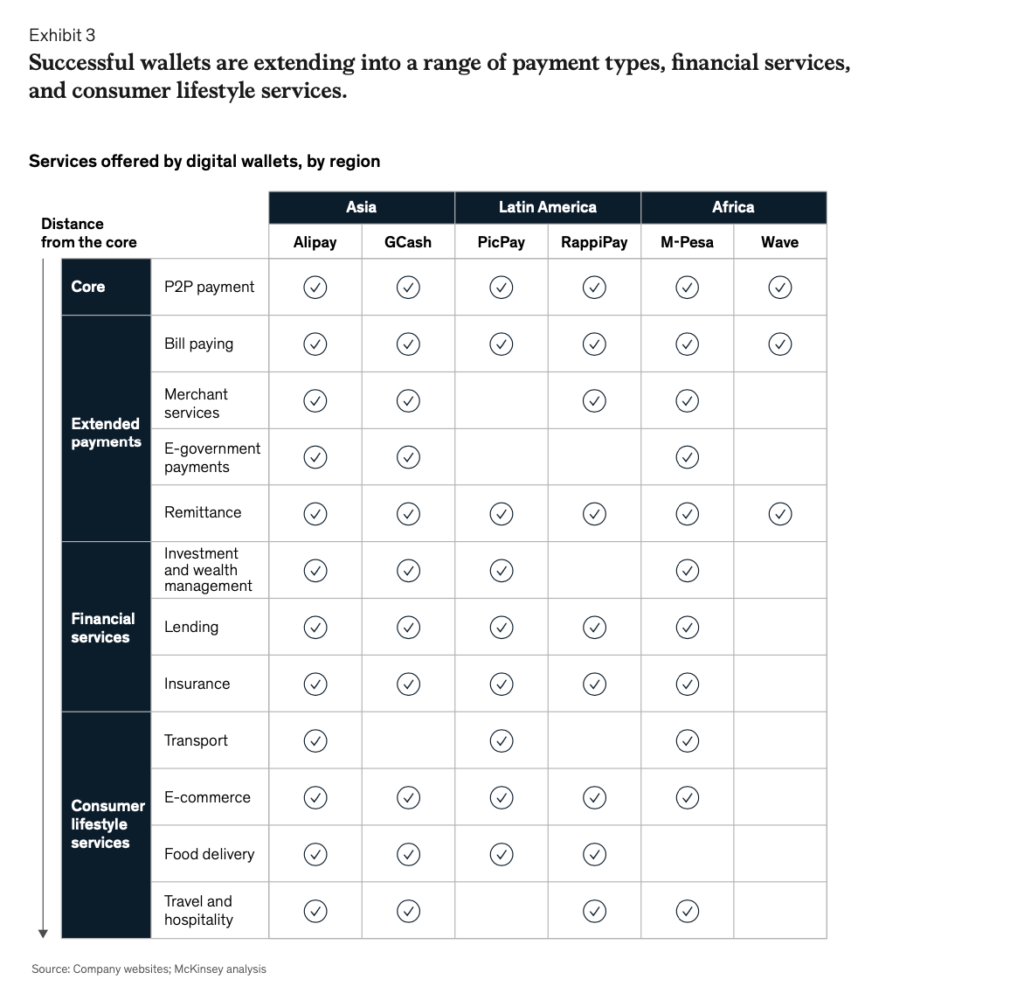
In the final chapter, the report examines how some of the fastest growth in digital payments over the past two years has been in emerging markets in Africa, Latin America, and Southeast Asia. In these areas, the pandemic accelerated shifts to contactless payments and e-commerce, and low banking penetration affords opportunities for payments providers to captureCapture capture The act of finalizing an authorized payment. Funds are transferred from the cardholder’s account to the merchant. untapped potential and reach underserved populations. Competition among banks, fintechs, telecom companies, and retailers has intensified as e-walletsWallets wallets See Digital Wallets. proliferate, instant bank transfers take off, and industry players form partnerships to access capabilities and broaden their customer base. The report explores which digital payments models are best placed to gain momentum in emerging markets, which monetization paths payments providers are likely to pursue, and what innovations may lie on the horizon.